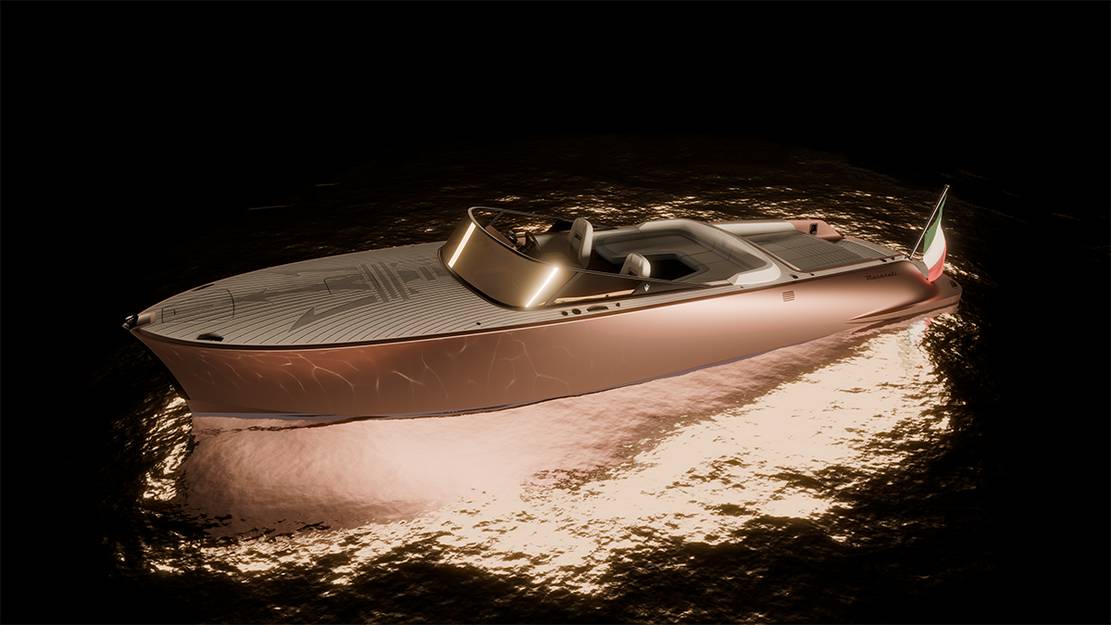
Maserati Tridente All-Electric Powerboat
Maserati Tridente all-electric powerboat is a 10.5-meter beauty perfect for leisurely cruises with up to eight guests.
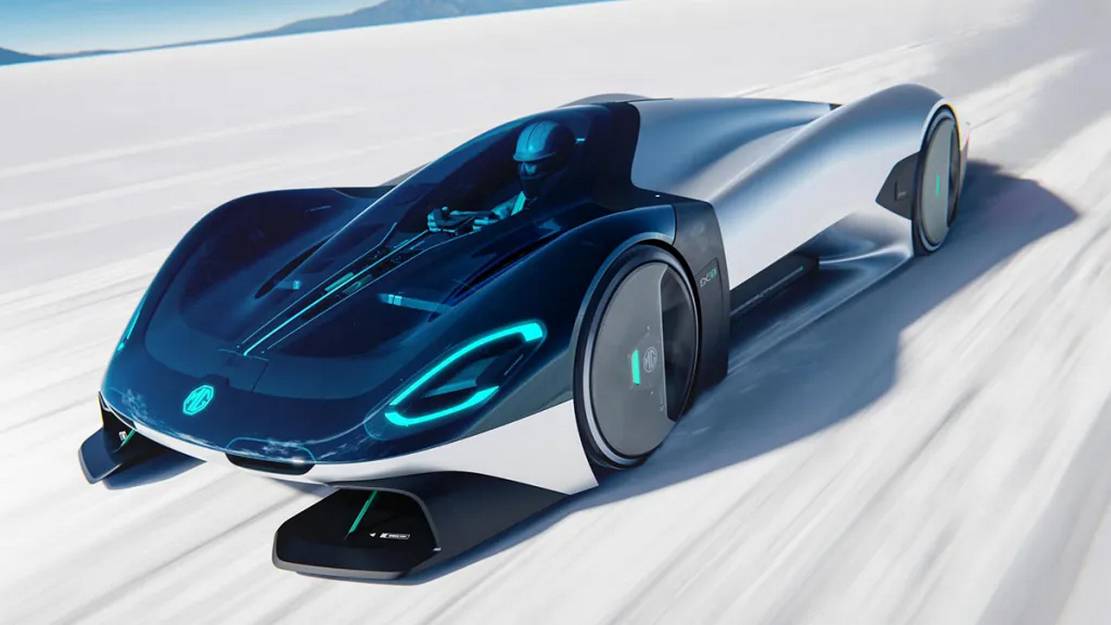
MG EXE181 Single-Seater Hypercar concept
The MG EXE181 single-seater hypercar concept was just unveiled for the Beijing Auto Show and came with a smooth and stretched-out design ending in a longtail.
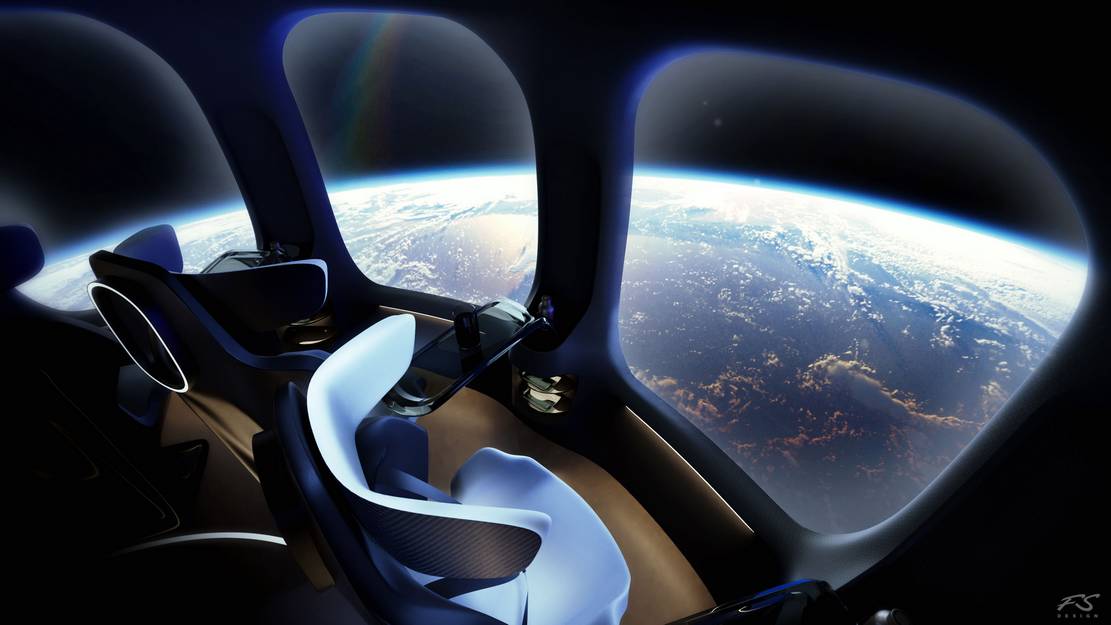
New Luxury Halo Space Capsule
The new luxury Halo Space Capsule offers a unique experience that takes you to the stratosphere.
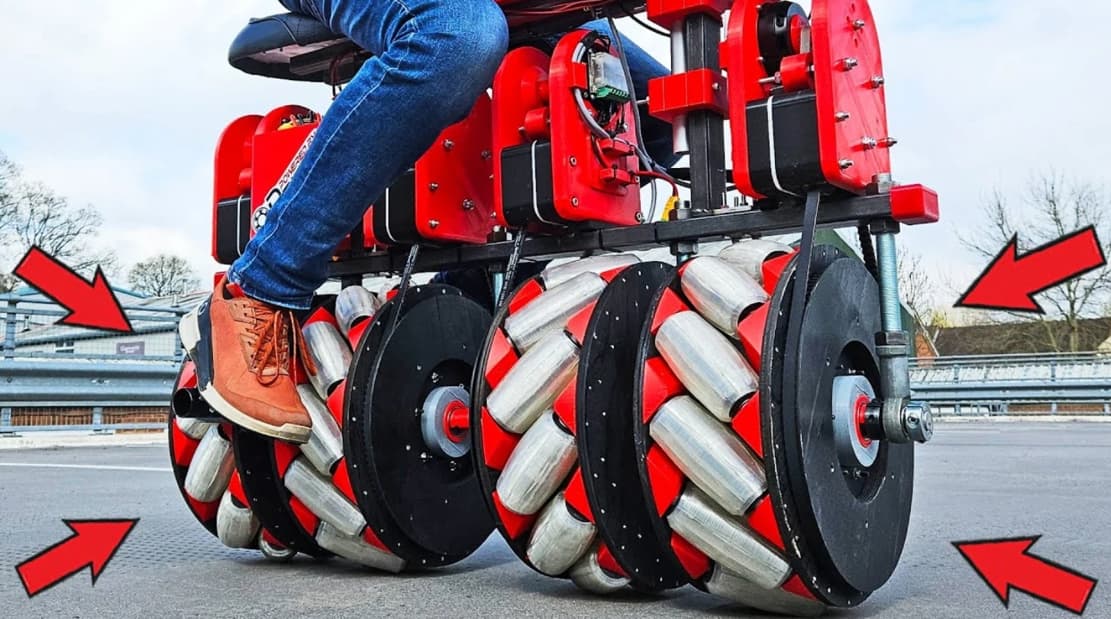
The crazy Screw Bike
This is a screw bike with two omni-wheels that can move it in any direction.
AI surpasses Humans in most benchmarks in Index report
The seventh edition of the AI Index report shows that Artificial Intelligence surpasses humans in most benchmarks.
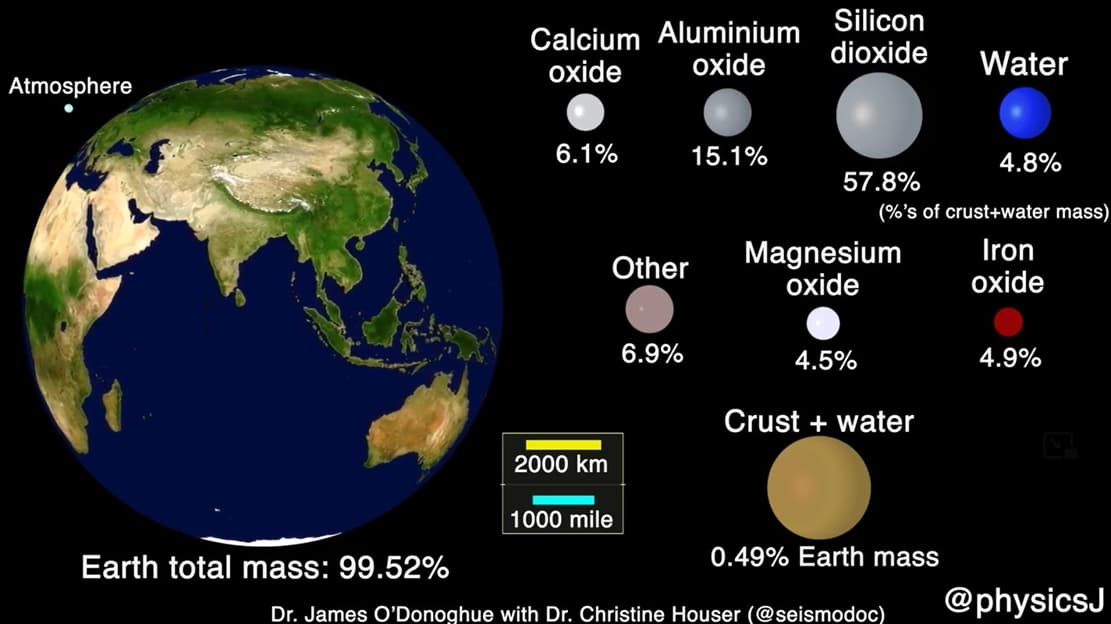
The Scale and Composition of the Earth’s Crust
The scale and composition of the Earth's crust, the layer upon which every living thing has ever lived.
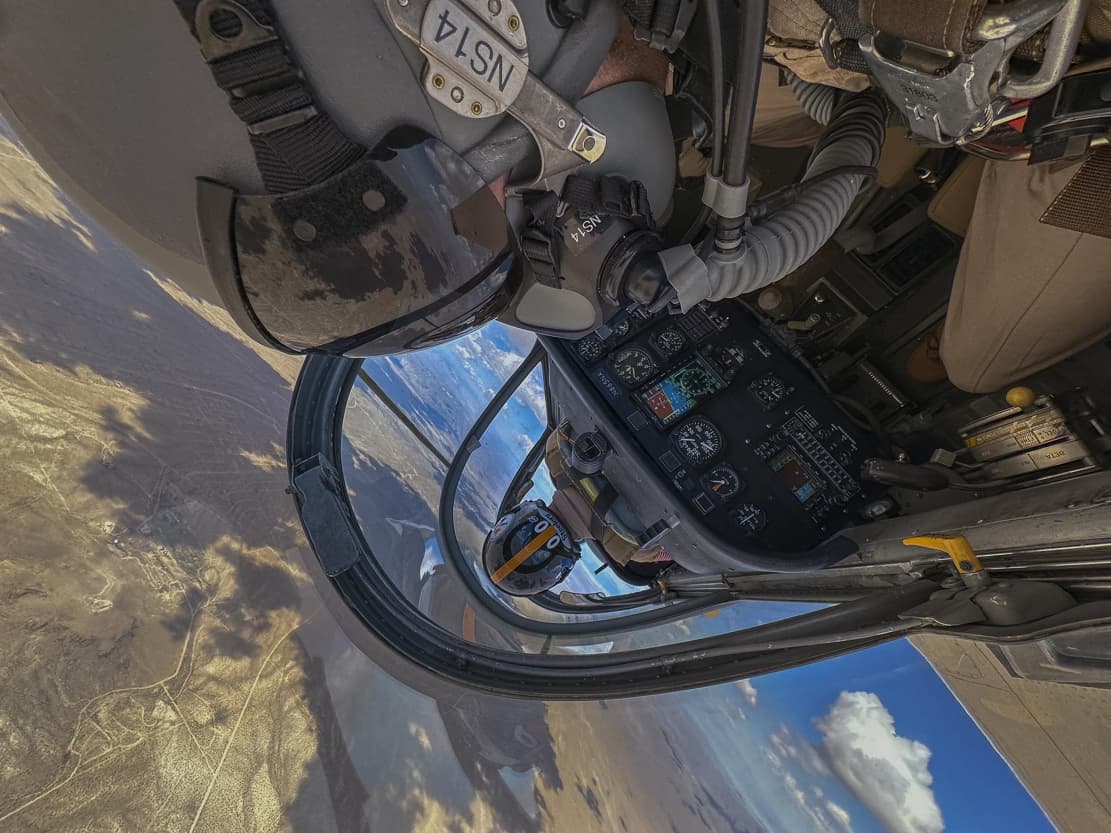
Honored Inverted In-Flight Image
NASA photographer Jim Ross was honored for a thrilling inverted in-flight aerobatic maneuvers image.
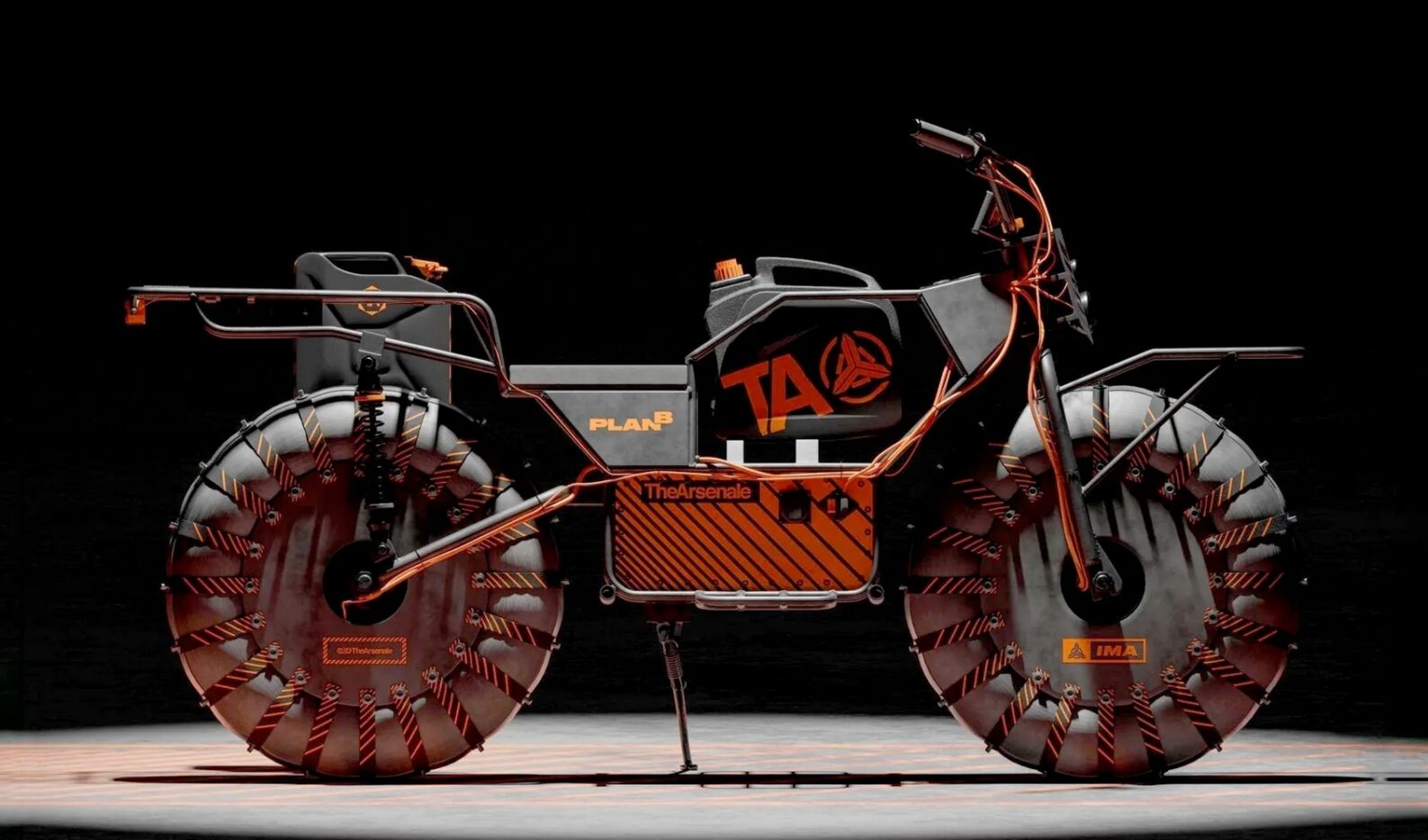
Arsenale ‘Plan B’ Hybrid Adventure electric bike
Arsenale introduced 'Plan B', a lightweight, long-range, 2-wheel-drive hybrid electric bike.
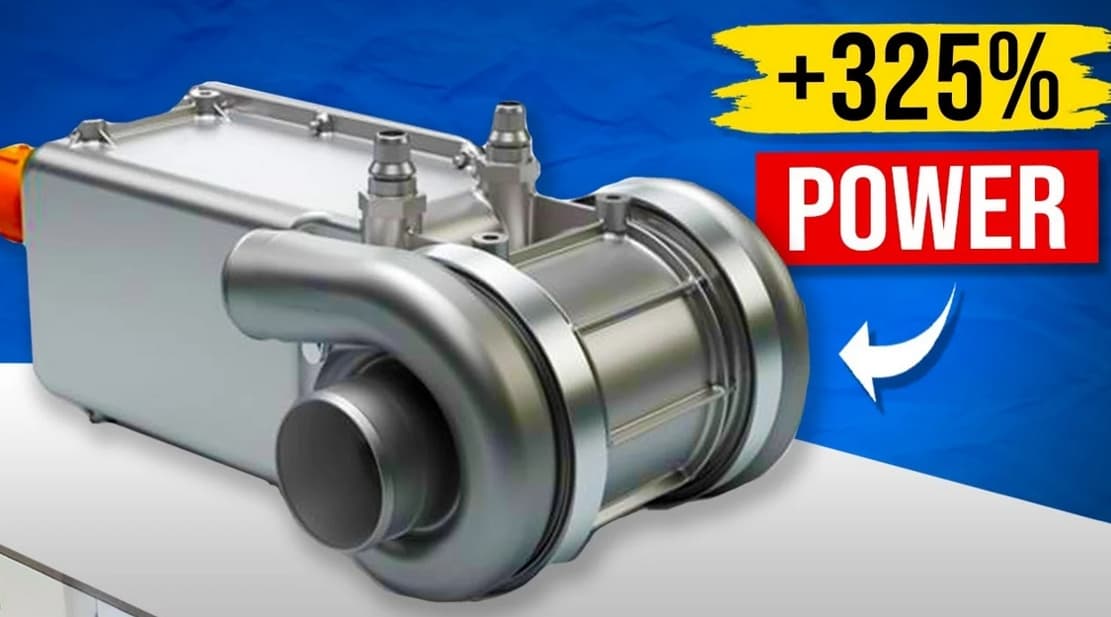
New Hydrogen Fuel Cells
New eco-friendly Hydrogen fuel cells pack more power, making long-distance hydrogen electric flights possible.
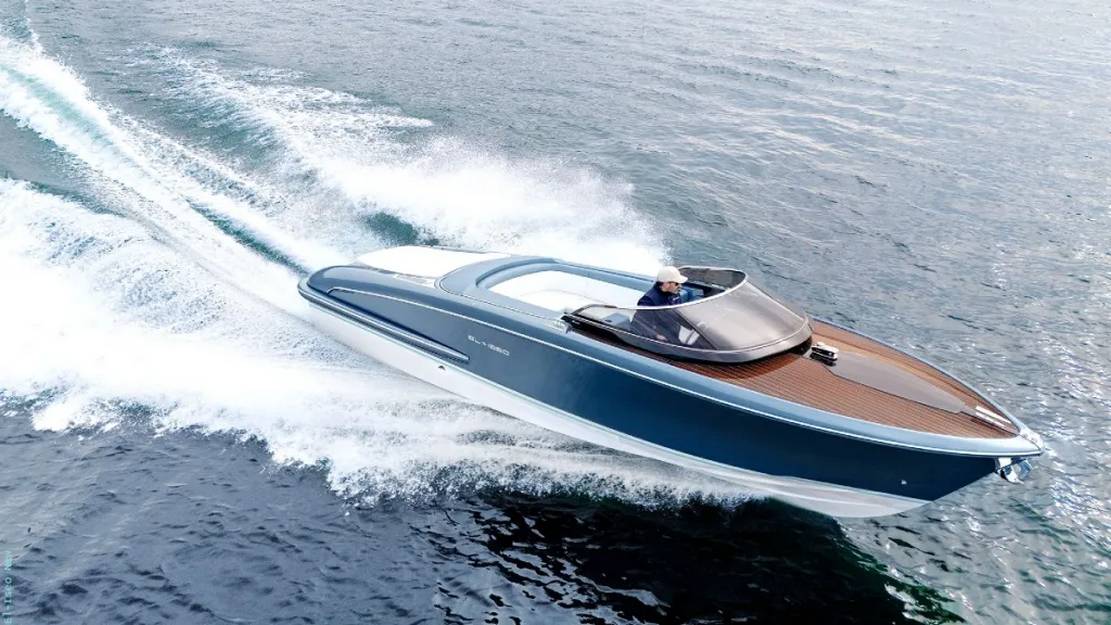
Riva El-Iseo Fully-Electric Motor Yacht
Riva's El-Iseo marks the famed boat builder's debut in fully electric motor yachts.