Scientists created first living robots designed by supercomputers, that are fully programmable.
UVM and Tufts team builds tiny ‘xenobots’ assembled from cells, promise advances from drug delivery to toxic waste clean-up.
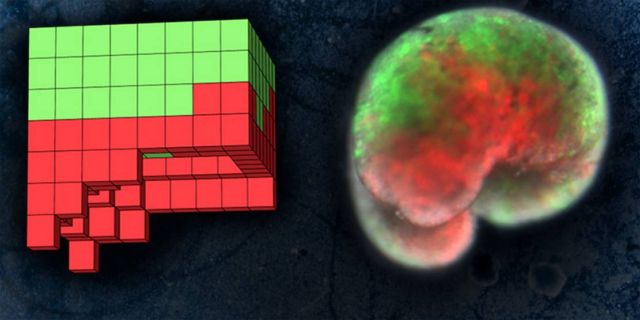
Above: On the left, the anatomical blueprint for a computer-designed organism, discovered on a UVM supercomputer. On the right, the living organism, built entirely from frog skin (green) and heart muscle (red) cells. The background displays traces carved by a swarm of these new-to-nature organisms as they move through a field of particulate matter. Credit Sam Kriegman, UVM
A book is made of wood. But it is not a tree. The dead cells have been repurposed to serve another need.
Now a team of scientists has repurposed living cells—scraped from frog embryos—and assembled them into entirely new life-forms. These millimeter-wide “xenobots” can move toward a target, perhaps pick up a payload (like a medicine that needs to be carried to a specific place inside a patient)—and heal themselves after being cut.
“These are novel living machines,” says Joshua Bongard, a computer scientist and robotics expert at the University of Vermont who co-led the new research. “They’re neither a traditional robot nor a known species of animal. It’s a new class of artifact: a living, programmable organism.”
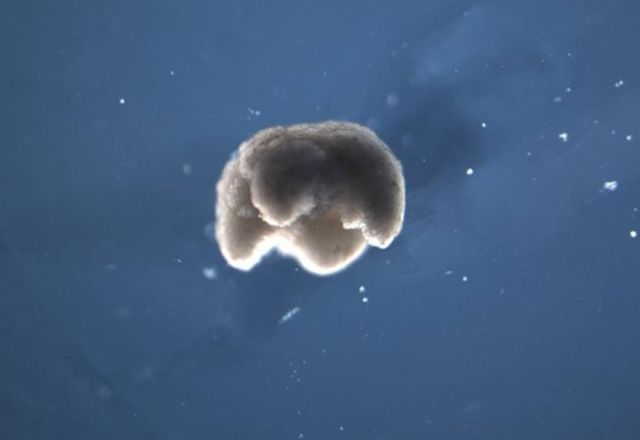
A manufactured quadruped organism, 650-750 microns in diameter—a bit smaller than a pinhead. Credit Douglas Blackiston, Tufts University
The new creatures were designed on a supercomputer at UVM—and then assembled and tested by biologists at Tufts University. “We can imagine many useful applications of these living robots that other machines can’t do,” says co-leader Michael Levin who directs the Center for Regenerative and Developmental Biology at Tufts, “like searching out nasty compounds or radioactive contamination, gathering microplastic in the oceans, traveling in arteries to scrape out plaque.”
The results of the new research were published January 13 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
source University of Vermont




Leave A Comment