A rare dynamic event of the death of a Red Giant Star, captured by scientists for the first time.
An international team of astronomers has witnessed a rare dynamic event foreshadowing the death of a red giant star – a discovery that reinforces predictions about our Sun’s ultimate demise.
Dr Meridith Joyce, an astronomer based at The Australian National University (ANU) co-led the study with Dr László Molnár and Dr László Kiss from the Konkoly Observatory of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. Dr Joyce said the star studied, T Ursae Minoris (T UMi), was similar to the Sun.
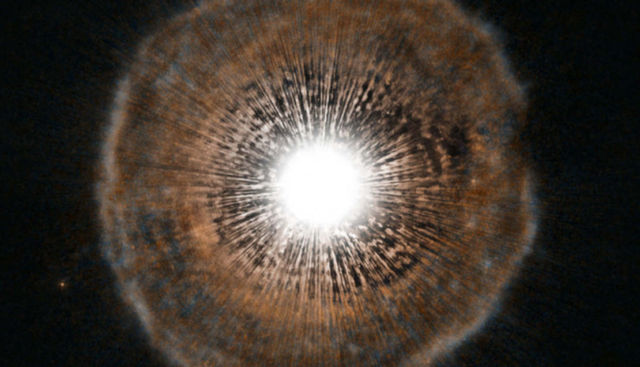
Above, the star U Camelopardalis that pulses out a shroud of dust and gas, like the red giant T Ursae Minoris. Credit ESA/Hubble, NASA and H. Olofsson.
“This has been one of the rare opportunities when the signs of ageing could be directly observed in a star over human timescales,” said Dr Joyce.
“We anticipate our Sun and T UMi will end their lives much more quietly and slowly compared with a supernova – a powerful and luminous explosion.”
The findings support the prediction that our Sun will turn into a red giant and then into an expanding and glowing ring-shaped shell of gas in five billion years, leaving behind a small white dwarf as a remnant, Dr Joyce said.
“It will become much bigger as it approaches death – eating Venus, Mercury and possibly the Earth in the process – before shrinking to become a white dwarf,” she said.
T UMi was born about 1.2 billion years ago, with a mass roughly twice that of our Sun, in the Little Bear constellation more than 3000 light years from Earth.
The team found that over the past few million years, during its last stage of life before its ultimate transition to a white dwarf, T UMi has been undergoing a series of pulses, whereby its size, brightness and temperature have fluctuated enormously.
“Energy production in T UMi has become unstable. During this phase, nuclear fusion flares up deep inside, causing ‘hiccups’ that we call thermal pulses.
source Australian National University



Leave A Comment