These are the first science results from NASA’s Juno Mission on Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system.
Early science results from NASA’s Juno mission to Jupiter portray, a complex, gigantic, turbulent world, with Earth-sized polar cyclones, plunging storm systems that travel deep into the heart of the gas giant, and a mammoth, lumpy magnetic field that may indicate it was generated closer to the planet’s surface than previously thought.
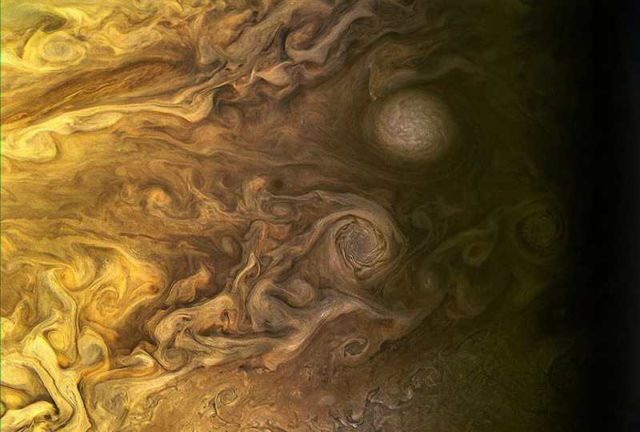
Above, Jupiter as seen by the Juno spacecraft on March 27, 2017. Credit NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill.
“We are excited to share these early discoveries, which help us better understand what makes Jupiter so fascinating,” said Diane Brown, Juno program executive at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “It was a long trip to get to Jupiter, but these first results already demonstrate it was well worth the journey.”
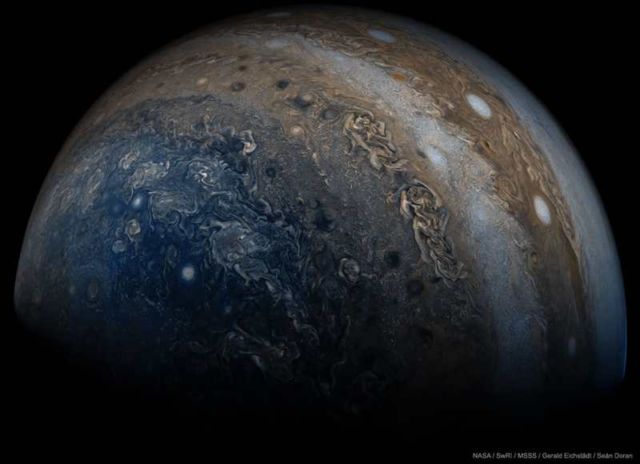
Image credit NASA, Juno, SwRI, MSSS, Gerald Eichstädt & Seán Doran
Juno launched on Aug. 5, 2011, entering Jupiter’s orbit on July 4, 2016. The findings from the first data-collection pass, which flew within about 2,600 miles (4,200 kilometers) of Jupiter’s swirling cloud tops on Aug. 27, are being published this week in two papers in the journal Science, as well as 44 papers in Geophysical Research Letters.
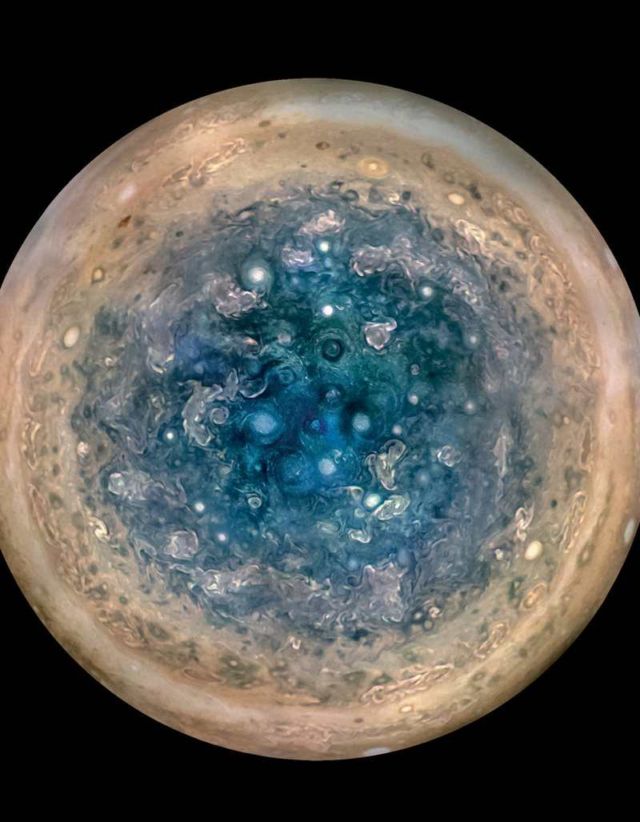
Jupiter’s south pole, as seen by NASA’s Juno spacecraft from an altitude of 32,000 miles (52,000 kilometers). The oval features are cyclones, up to 600 miles (1,000 kilometers) in diameter. Multiple images taken with the JunoCam instrument on three separate orbits were combined to show all areas in daylight, enhanced color, and stereographic projection. Credits NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Betsy Asher Hall/Gervasio Robles
“We knew, going in, that Jupiter would throw us some curves,” said Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio. “But now that we are here we are finding that Jupiter can throw the heat, as well as knuckleballs and sliders. There is so much going on here that we didn’t expect that we have had to take a step back and begin to rethink of this as a whole new Jupiter.”
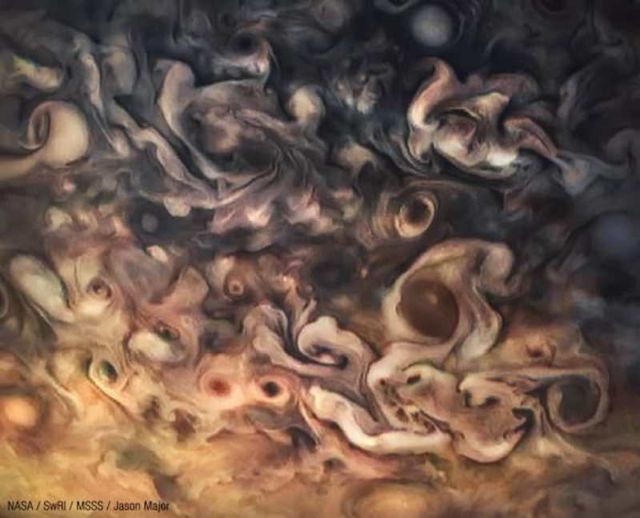
Uncalibrated, processed raw image from Juno’s Perijove 6 pass of Jupiter on May 19, 2017. Credit NASA/SwRI/MSSS/Jason Major.
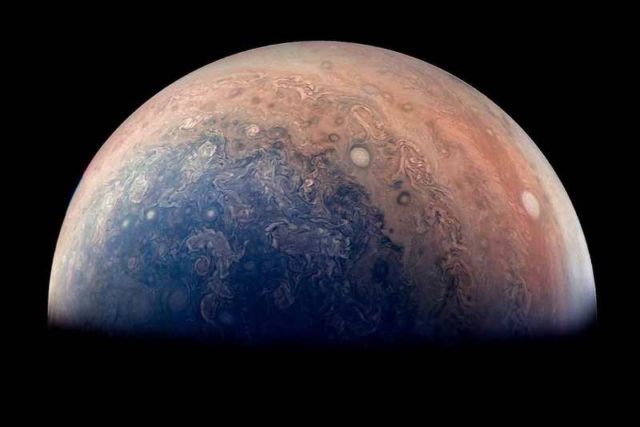
Image credit NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Gabriel Fiset








Leave A Comment