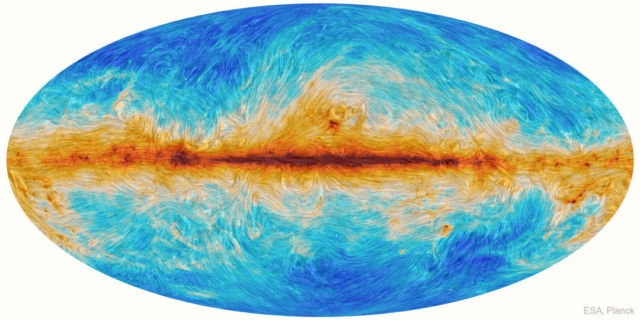
Analyses of observations by ESA’s Planck satellite of emission by small magnetically-aligned dust grains reveal previously unknown magnetic field structures in our Milky Way Galaxy — as shown by the curvy lines in the featured full-sky image.
The dark red shows the plane of the Milky Way, where the concentration of dust is the highest. The huge arches above the plane are likely remnants of past explosive events from our Galaxy’s core, conceptually similar to magnetic loop-like structures seen in our Sun’s atmosphere. The curvy streamlines align with interstellar filaments of neutral hydrogen gas and provide tantalizing evidence that magnetic fields may supplement gravity in not only in shaping the interstellar medium, but in forming stars.
How magnetism affected our Galaxy’s evolution will likely remain a topic of research for years to come.
source APOD



Leave A Comment