NASA’s Perseverance Mars Rover generates Oxygen from Red Planet for the first time.
The growing list of “firsts” for Perseverance, NASA’s newest six-wheeled robot on the Martian surface, includes converting some of the Red Planet’s thin, carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere into oxygen.
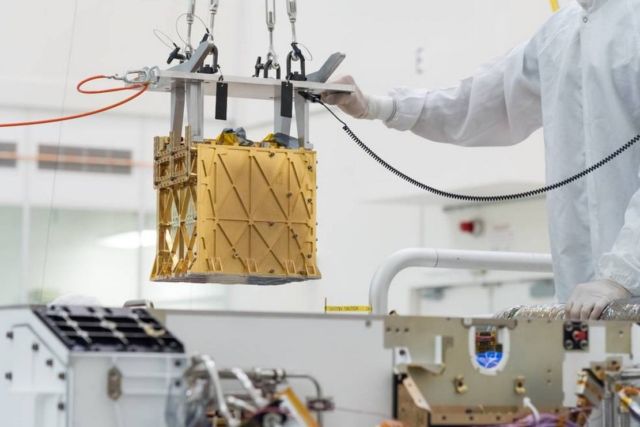
Above: Technicians at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory lower the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) instrument into the belly of the Perseverance rover. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
A toaster-size, experimental instrument aboard Perseverance called the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) accomplished the task. The test took place April 20, the 60th Martian day, or sol, since the mission landed Feb. 18.
While the technology demonstration is just getting started, it could pave the way for science fiction to become science fact – isolating and storing oxygen on Mars to help power rockets that could lift astronauts off the planet’s surface. Such devices also might one day provide breathable air for astronauts themselves. MOXIE is an exploration technology investigation – as is the Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA) weather station – and is sponsored by NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD) and Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate.
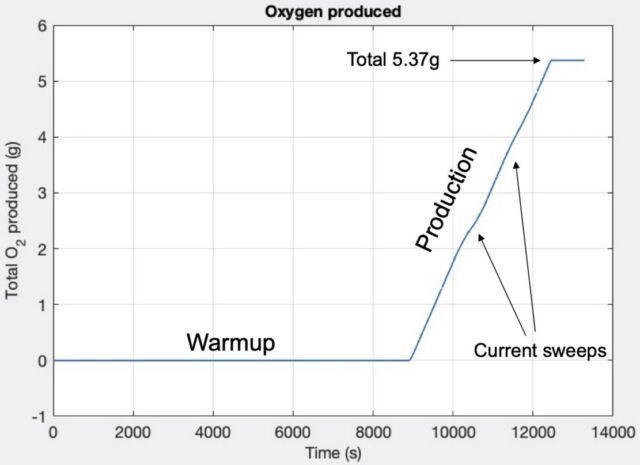
After a 2-hour warmup period MOXIE began producing oxygen at a rate of 6 grams per hour. The was reduced two times during the run (labeled as “current sweeps”) in order to assess the status of the instrument. After an hour of operation the total oxygen produced was about 5.4 grams, enough to keep an astronaut healthy for about 10 minutes of normal activity. Credits: MIT Haystack Observatory
“This is a critical first step at converting carbon dioxide to oxygen on Mars,” said Jim Reuter, associate administrator for STMD. “MOXIE has more work to do, but the results from this technology demonstration are full of promise as we move toward our goal of one day seeing humans on Mars. Oxygen isn’t just the stuff we breathe. Rocket propellant depends on oxygen, and future explorers will depend on producing propellant on Mars to make the trip home.”
source NASA






Leave A Comment