NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover has been attached to the top of the rocket that will send it toward the Red Planet this summer.
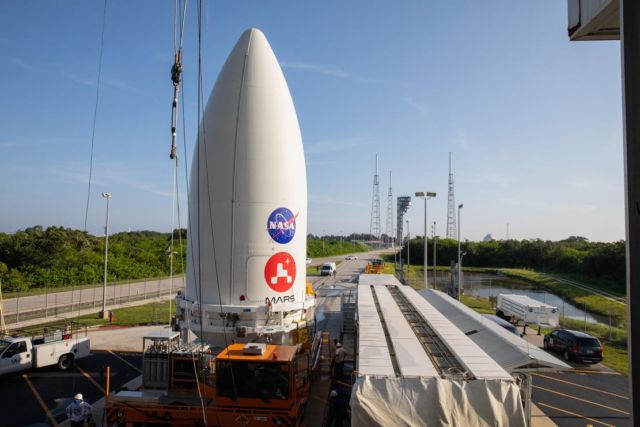
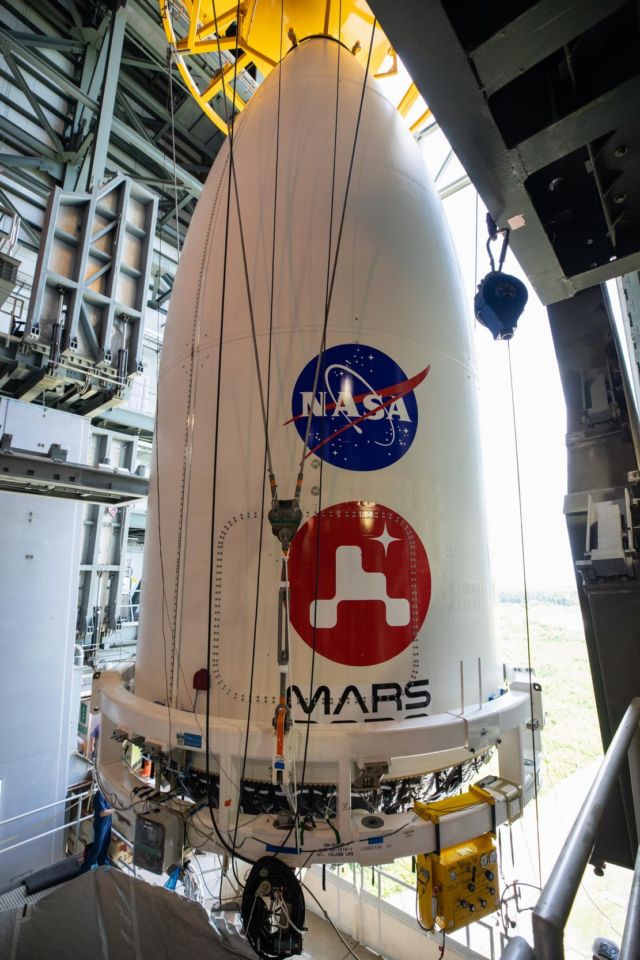
Encased in the nose cone that will protect it during launch, the rover and the rest of the Mars 2020 spacecraft – the aeroshell, cruise stage, and descent stage – were affixed to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster on Tuesday, July 7, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Central Florida.
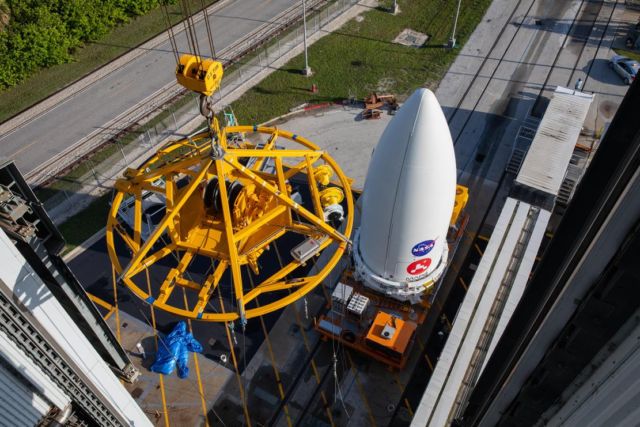
The process began when a 60-ton hoist on the roof of the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 lifted the nose cone, otherwise known as the payload fairing, 129 feet (39 meters) to the top of the waiting rocket. There, engineers made the physical and electrical connections that will remain between booster and spacecraft until about 50 to 60 minutes after launch, when the two are pyrotechnically separated and Perseverance is on its way.
“I have seen my fair share of spacecraft being lifted onto rockets,” said John McNamee, project manager for the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mission at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “But this one is special because there are so many people who contributed to this moment. To each one of them I want to say, we got here together, and we’ll make it to Mars the same way.”
With the mating of spacecraft and booster complete, the final testing of the two (separately and as one unit) will be underway. Then two days before the July 30 launch, the Atlas V will leave the Vertical Integration Facility for good. Traveling by rail, it will cover the 1,800 feet (550 meters) to the launch pad in about 40 minutes. From there, Perseverance has about seven months and 290 million miles (467 million kilometers) to go before arriving at Mars.
source NASA JPL







Leave A Comment