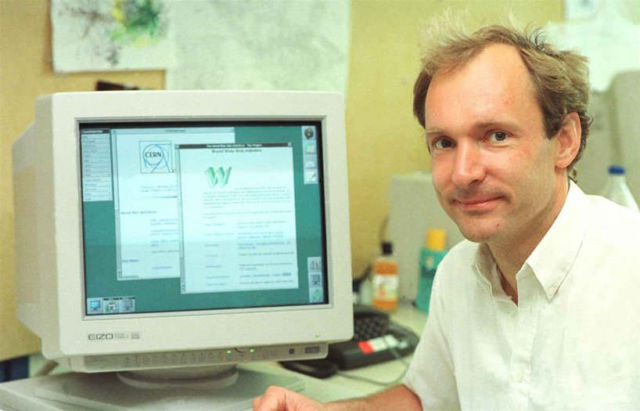
In the occasion of World Wide Web’s 30th birthday, Web inventor Sir Tim Berners-Lee reflects on how the web has changed our world.
Today, 30 years on from my original proposal for an information management system, half the world is online. It’s a moment to celebrate how far we’ve come, but also an opportunity to reflect on how far we have yet to go.
Above, Sir Tim Berners-Lee launches the Contract for the Web at Web Summit 2018. Credit Webfoundation
The web has become a public square, a library, a doctor’s office, a shop, a school, a design studio, an office, a cinema, a bank, and so much more. Of course with every new feature, every new website, the divide between those who are online and those who are not increases, making it all the more imperative to make the web available for everyone.
And while the web has created opportunity, given marginalised groups a voice, and made our daily lives easier, it has also created opportunity for scammers, given a voice to those who spread hatred, and made all kinds of crime easier to commit.
Against the backdrop of news stories about how the web is misused, it’s understandable that many people feel afraid and unsure if the web is really a force for good. But given how much the web has changed in the past 30 years, it would be defeatist and unimaginative to assume that the web as we know it can’t be changed for the better in the next 30. If we give up on building a better web now, then the web will not have failed us. We will have failed the web.
Sir Tim Berners-Lee. Credit Webfoundation
To tackle any problem, we must clearly outline and understand it. I broadly see three sources of dysfunction affecting today’s web:
- Deliberate, malicious intent, such as state-sponsored hacking and attacks, criminal behaviour, and online harassment.
- System design that creates perverse incentives where user value is sacrificed, such as ad-based revenue models that commercially reward clickbait and the viral spread of misinformation.
- Unintended negative consequences of benevolent design, such as the outraged and polarised tone and quality of online discourse.
Read more at webfoundation






Leave A Comment