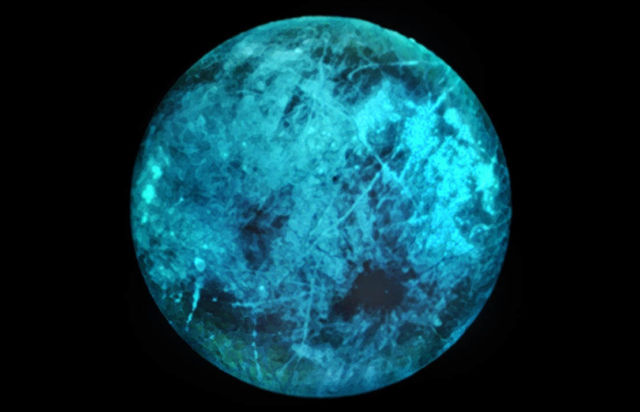
Radiation from Jupiter makes its moon Europa, to glow.
This illustration of Jupiter’s moon Europa shows how the icy surface may glow on its nightside, the side facing away from the Sun. Variations in the glow and the color of the glow itself could reveal information about the composition of ice on Europa’s surface.
New lab experiments re-create the environment of Europa and find that the icy moon shines, even on its nightside. The effect is more than just a cool visual.
As the icy, ocean-filled moon Europa orbits Jupiter, it withstands a relentless pummeling of radiation. Jupiter zaps Europa’s surface night and day with electrons and other particles, bathing it in high-energy radiation. But as these particles pound the moon’s surface, they may also be doing something otherworldly: making Europa glow in the dark.
New research from scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California details for the first time what the glow would look like, and what it could reveal about the composition of ice on Europa’s surface. Different salty compounds react differently to the radiation and emit their own unique glimmer. To the naked eye, this glow would look sometimes slightly green, sometimes slightly blue or white and with varying degrees of brightness, depending on what material it is.
“We were able to predict that this nightside ice glow could provide additional information on Europa’s surface composition. How that composition varies could give us clues about whether Europa harbors conditions suitable for life,” said JPL’s Murthy Gudipati, lead author of the work published Nov. 9 in Nature Astronomy.
Image credit NASA/JPL-Caltech
source JPL/NASA



Leave A Comment