Astronomers discovered six galaxies trapped in the web of a supermassive black hole.
With the help of ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), astronomers have found six galaxies lying around a supermassive black hole, the first time such a close grouping has been seen within the first billion years of the Universe.
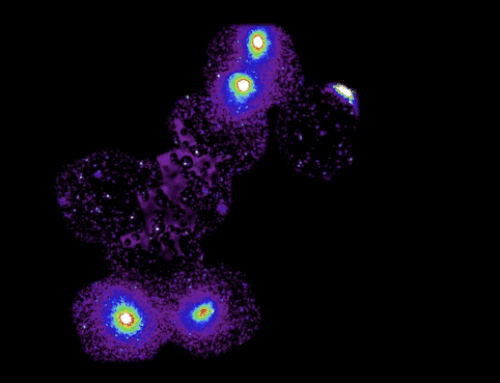
This artist’s impression shows the central black hole and the galaxies trapped in its gas web. The black hole, which together with the disc around it is known as quasar SDSS J103027.09+052455.0, shines brightly as it engulfs matter around it.
“This research was mainly driven by the desire to understand some of the most challenging astronomical objects — supermassive black holes in the early Universe. These are extreme systems and to date we have had no good explanation for their existence,” said Marco Mignoli, an astronomer at the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) in Bologna, Italy, and lead author of the new research published today in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The new observations with ESO’s VLT revealed several galaxies surrounding a supermassive black hole, all lying in a cosmic “spider’s web” of gas extending to over 300 times the size of the Milky Way. “The cosmic web filaments are like spider’s web threads,” explains Mignoli. “The galaxies stand and grow where the filaments cross, and streams of gas — available to fuel both the galaxies and the central supermassive black hole — can flow along the filaments.”
The light from this large web-like structure, with its black hole of one billion solar masses, has travelled to us from a time when the Universe was only 0.9 billion years old. “Our work has placed an important piece in the largely incomplete puzzle that is the formation and growth of such extreme, yet relatively abundant, objects so quickly after the Big Bang,” says co-author Roberto Gilli, also an astronomer at INAF in Bologna, referring to supermassive black holes.
source ESO



Leave A Comment