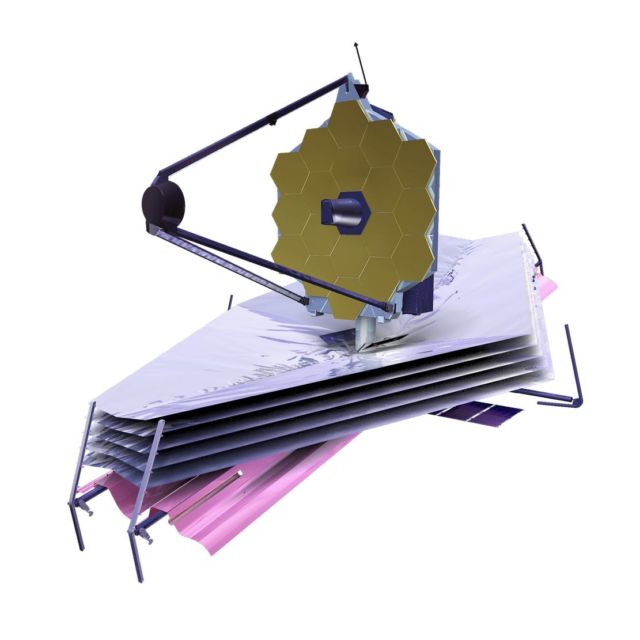
NASA plans to launch the James Webb Space Telescope into orbit Dec. 18, 2021, to serve as the premier deep space observatory for the next decade.
The agency set the new target launch date in coordination with Arianespace after Webb recently and successfully completed its rigorous testing regimen – a major turning point for the mission. The new date also follows Arianespace successfully launching an Ariane 5 rocket in late July and scheduling a launch that will precede Webb. The July launch was the first for an Ariane 5 since August 2020.
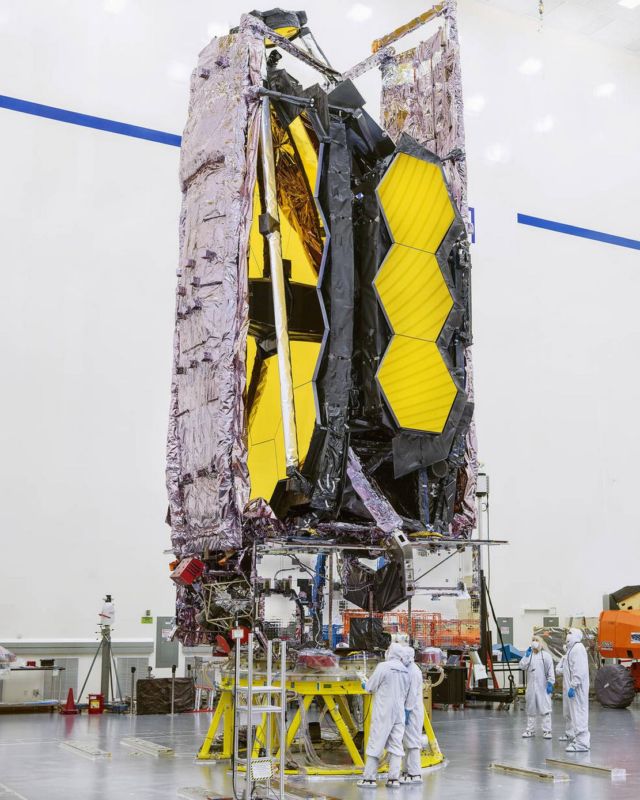
Image: NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is seen here being prepared for shipment to its launch site. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn
Webb, an international program led by NASA with its partners ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency, will launch on an Ariane 5 from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana on the northeastern coast of South America. ESA is providing the Ariane 5.
The highly complex space telescope is currently resting in its final stow configuration at Northrop Grumman’s facilities in Redondo Beach, California.
“Webb is an exemplary mission that signifies the epitome of perseverance,” said Gregory L. Robinson, Webb’s program director at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “I am inspired by our dedicated team and our global partnerships that have made this incredible endeavor possible. Together, we’ve overcome technical obstacles along the way as well as challenges during the coronavirus pandemic. I also am grateful for the steadfast support of Congress. Now that we have an observatory and a rocket ready for launch, I am looking forward to the big day and the amazing science to come.”
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or “Webb”) is a joint NASA–ESA–CSA space telescope that is planned to succeed the Hubble Space Telescope as NASA’s flagship astrophysics mission. The JWST will provide improved infrared resolution and sensitivity over Hubble, and will enable a broad range of investigations across the fields of astronomy and cosmology, including observing some of the most distant events and objects in the universe, such as the formation of the first galaxies.
source NASA





Leave A Comment