Thousands of mysterious holes discovered in the Pacific ocean floor off the Californian coast.
During a recent survey of the deep seafloor off Big Sur, MBARI researchers discovered thousands of mysterious holes or pits in the seafloor. Scientists and resource managers want to understand how these pits formed because this area is the site of a proposed wind-energy farm.
Above: Seafloor map showing pockmark and micro-depressions in the seafloor off Big Sur. Image: © 2019 MBARI
Researchers Eve Lundsten and Charles Paull describe their discovery this week at the Fall 2019 meeting of the American Geophysical Union in San Francisco.
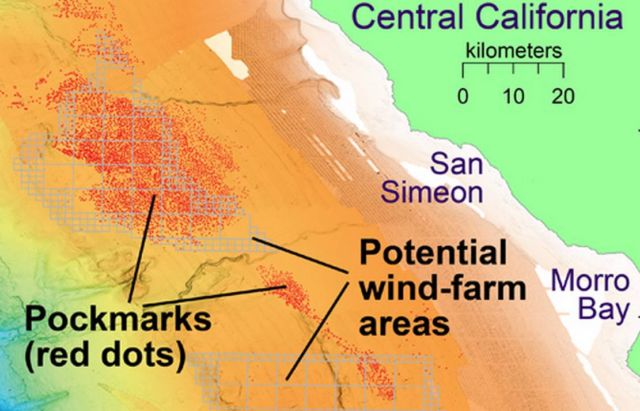 Map showing the locations of some of the pockmarks and proposed wind-farm areas off Central California. Image: © 2019 MBARI
Map showing the locations of some of the pockmarks and proposed wind-farm areas off Central California. Image: © 2019 MBARI
The researchers found two different sizes of holes. The larger ones, known as pockmarks, average 175 meters (almost 600 feet) across and five meters (16 feet) deep, and are nearly circular and fairly evenly spaced. Some of these pockmarks were initially discovered by MBARI scientists in 1999 during a seafloor survey using ship-mounted sonar. Over the last few years, additional surveys by MBARI and other organizations revealed over 5,200 pockmarks spread out over 1,300 square kilometers (500 square miles), making this area the largest known pockmark field in North America.
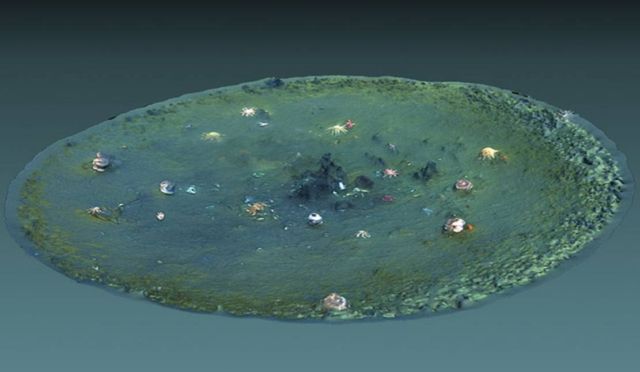 Computer-generated 3D view of a micro-depression created using underwater video from MBARI’s remotely operated vehicle Doc Ricketts. Image: Ben Erwin © 2019 MBARI
Computer-generated 3D view of a micro-depression created using underwater video from MBARI’s remotely operated vehicle Doc Ricketts. Image: Ben Erwin © 2019 MBARI
More recently, MBARI conducted detailed seafloor surveys using sonar mounted on autonomous underwater vehicles. These surveys revealed thousands of smaller pits, which they termed micro-depressions. The micro-depressions average just 11 meters (36 feet) across and one meter (three feet) deep. They have steeper sides than the pockmarks and are often elongated in one direction.
Seafloor pockmarks have been found elsewhere around the world, and have been associated with releases of methane gas or other fluids from the seafloor. Such methane releases could potentially cause the seafloor to be unstable, which could pose risks for structures such as offshore oil platforms or wind turbines. However MBARI researchers found no evidence of methane in the sediment or seawater in this region. In fact, sonar data showing layers of seafloor sediments suggest that these pockmarks have been inactive for the last 50,000 years.
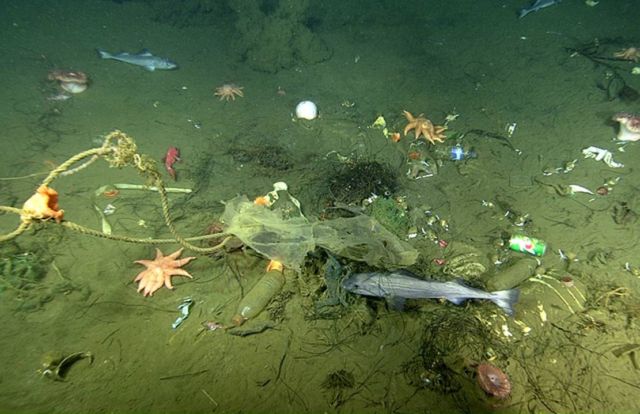 Close-up view of the seafloor inside a micro-depression, showing trash, rocks, seafloor animals, and fish. Image: © 2019 MBARI
Close-up view of the seafloor inside a micro-depression, showing trash, rocks, seafloor animals, and fish. Image: © 2019 MBARI
The researchers hypothesize that the micro-depressions are relatively recent features that were were excavated by local seafloor currents. Because the sediment on the seafloor in this area is so soft and “fluffy,” the researchers speculate that even the movements of fish hiding out in the micro-depressions could stir up the sediment, allowing it to be carried away by currents.
source MBARI






Leave A Comment