Cutting-edge VLTI GRAVITY instrument using optical interferometry, breaks new ground in exoplanet imaging, by revealing details of a storm-wracked exoplanet.
The GRAVITY instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI) has made the first direct observation of an exoplanet using optical interferometry. This method revealed a complex exoplanetary atmosphere with clouds of iron and silicates swirling in a planet-wide storm. The technique presents unique possibilities for characterising many of the exoplanets known today.
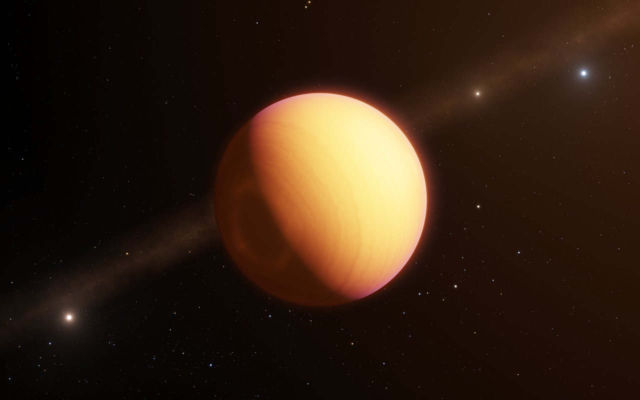
Above, this artist’s impression shows the observed exoplanet, which goes by the name HR8799e. Credit:ESO/L. Calçada
This result was announced today in a letter in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics by the GRAVITY Collaboration, in which they present observations of the exoplanet HR8799e using optical interferometry. The exoplanet was discovered in 2010 orbiting the young main-sequence star HR8799, which lies around 129 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Pegasus.
Today’s result, which reveals new characteristics of HR8799e, required an instrument with very high resolution and sensitivity. GRAVITY can use ESO’s VLT’s four unit telescopes to work together to mimic a single larger telescope using a technique known as interferometry. This creates a super-telescope — the VLTI — that collects and precisely disentangles the light from HR8799e’s atmosphere and the light from its parent star.
HR8799e is a ‘super-Jupiter’, a world unlike any found in our Solar System, that is both more massive and much younger than any planet orbiting the Sun. At only 30 million years old, this baby exoplanet is young enough to give scientists a window onto the formation of planets and planetary systems. The exoplanet is thoroughly inhospitable — leftover energy from its formation and a powerful greenhouse effect heat HR8799e to a hostile temperature of roughly 1000 °C.
source ESO





Leave A Comment